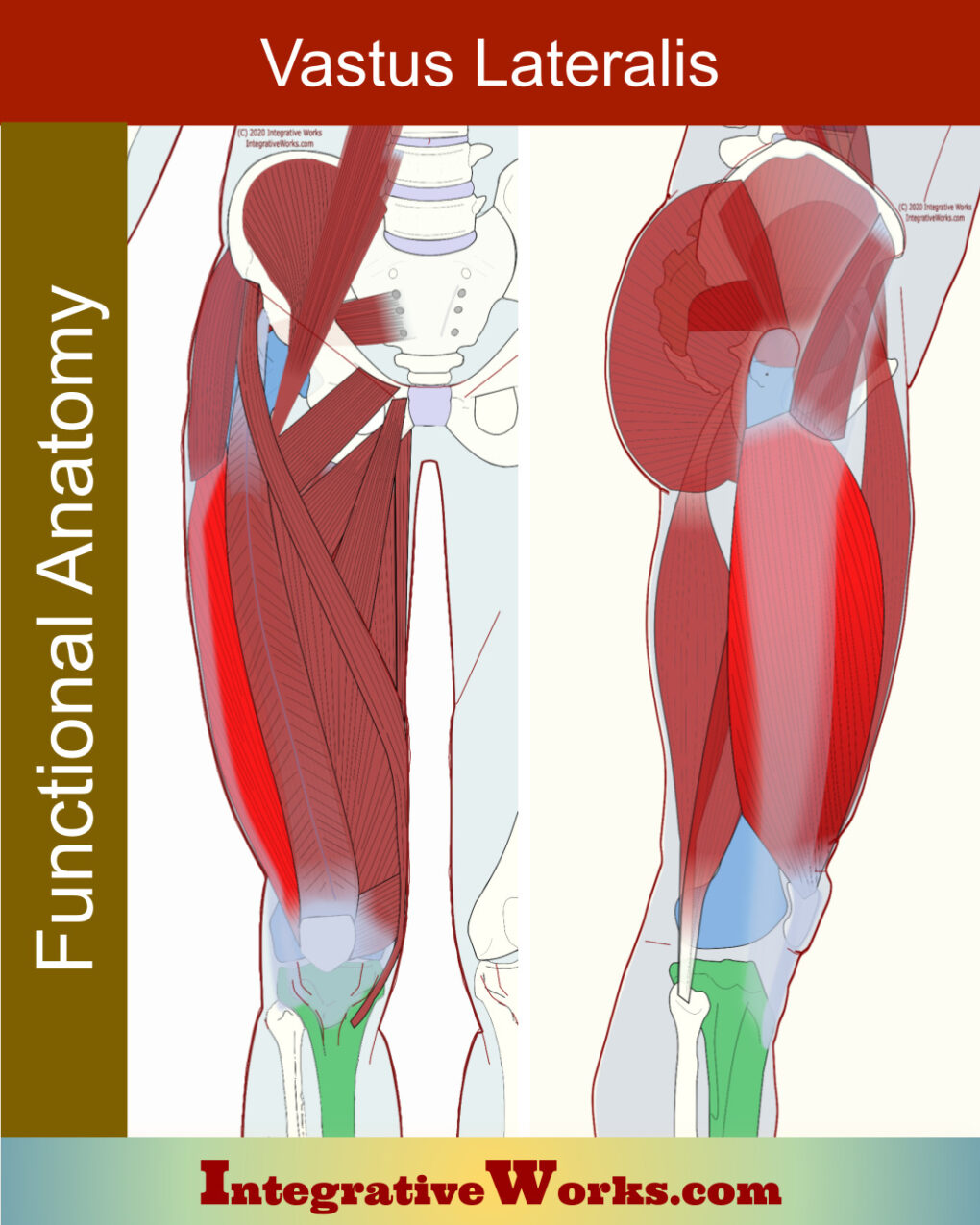
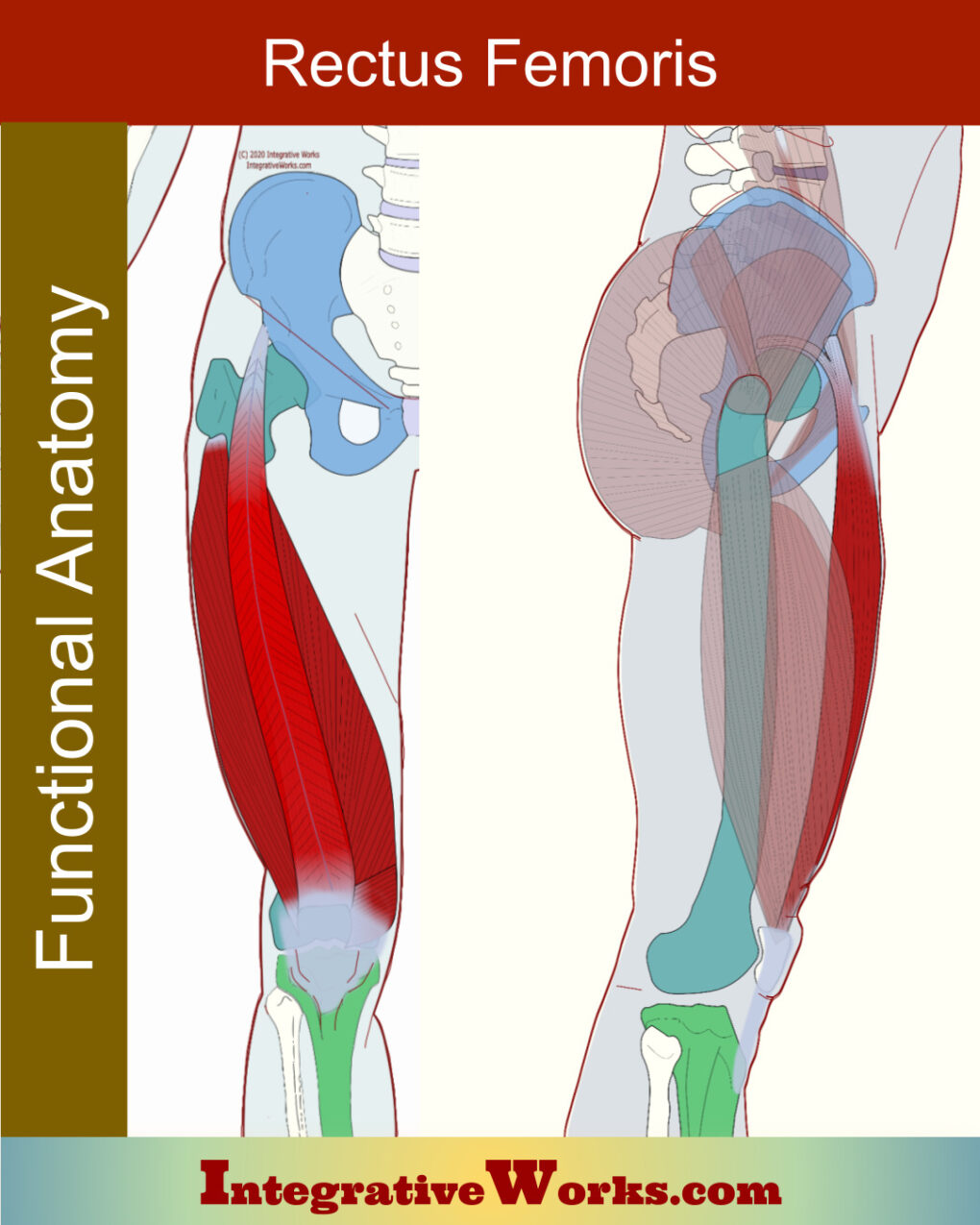
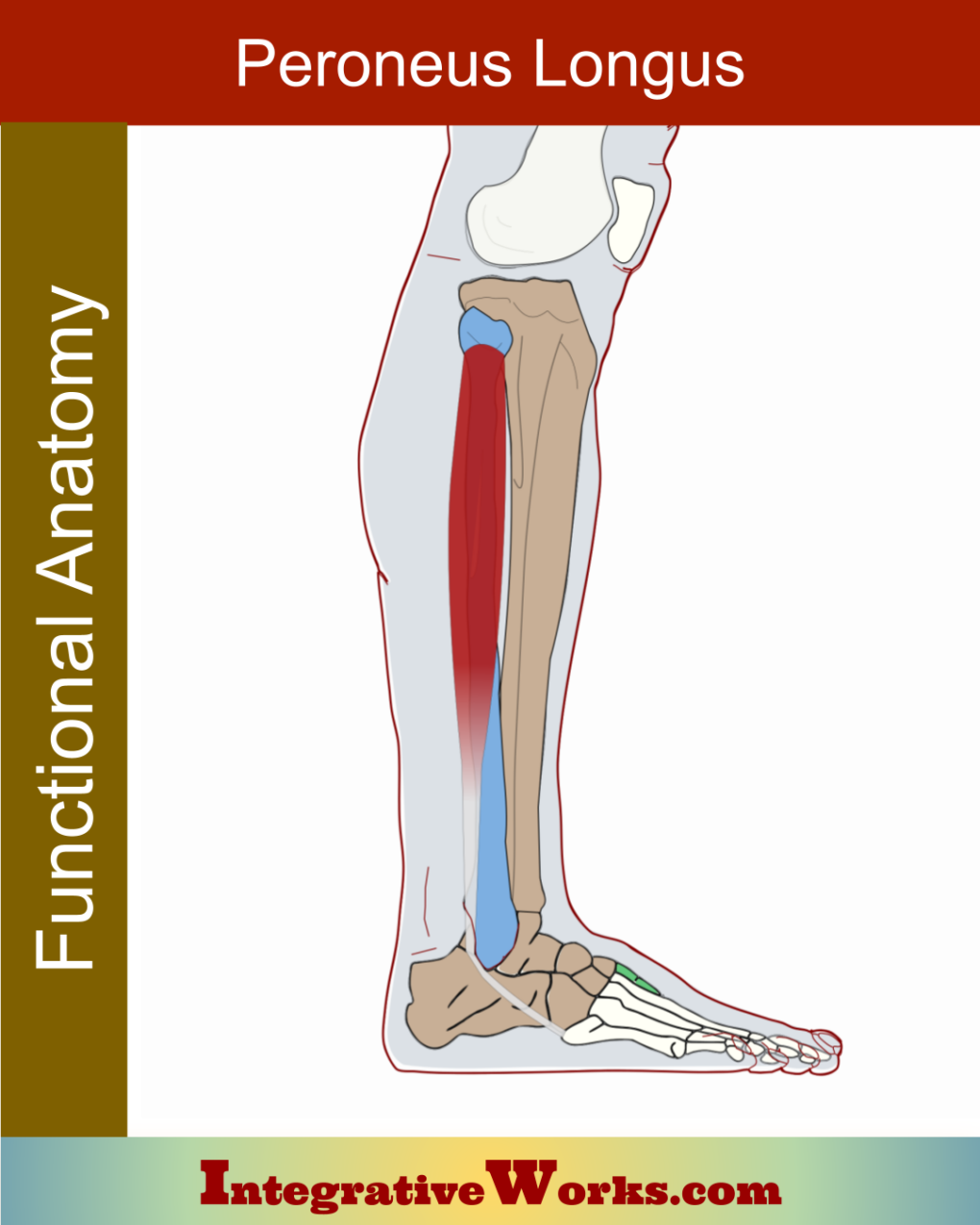
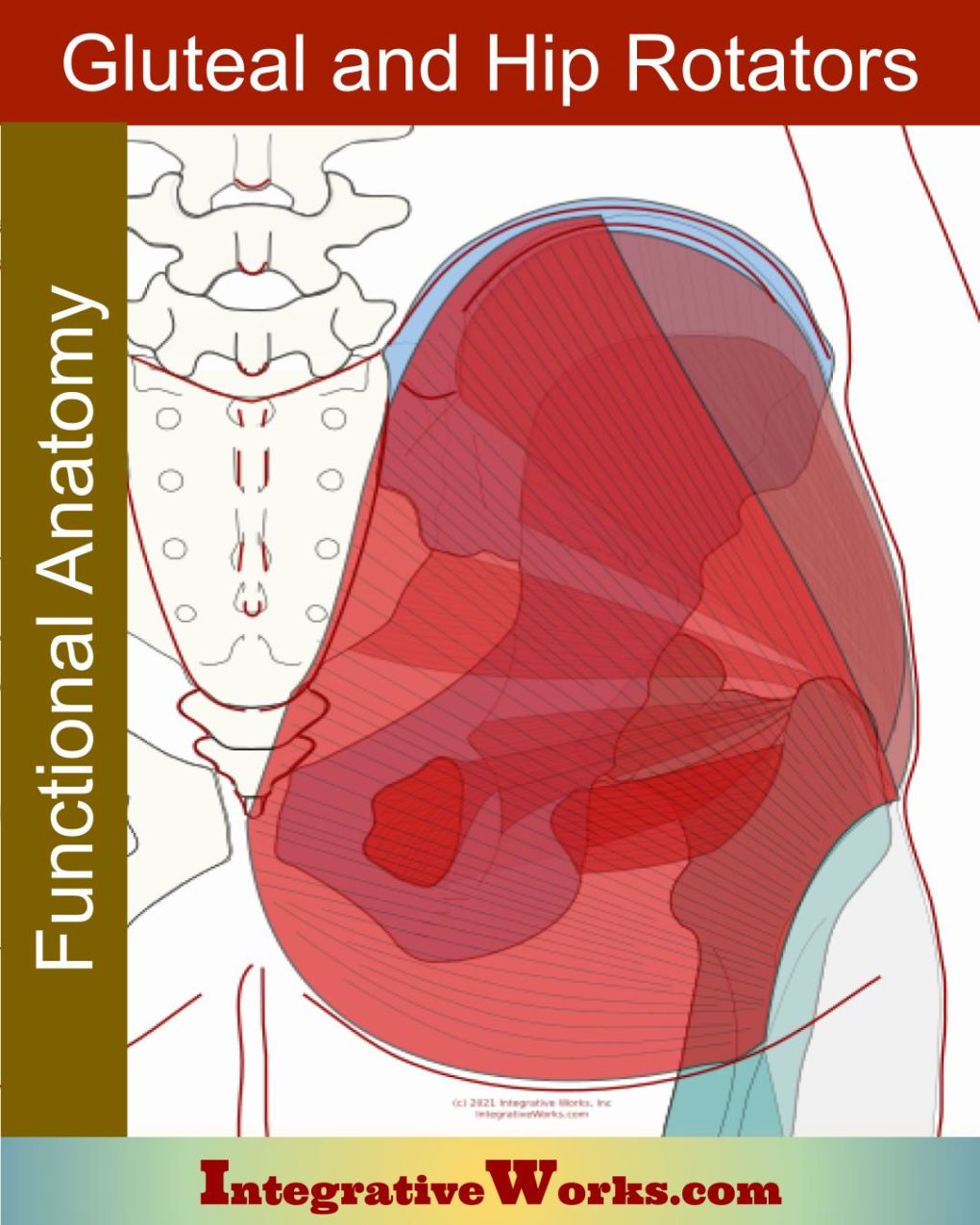
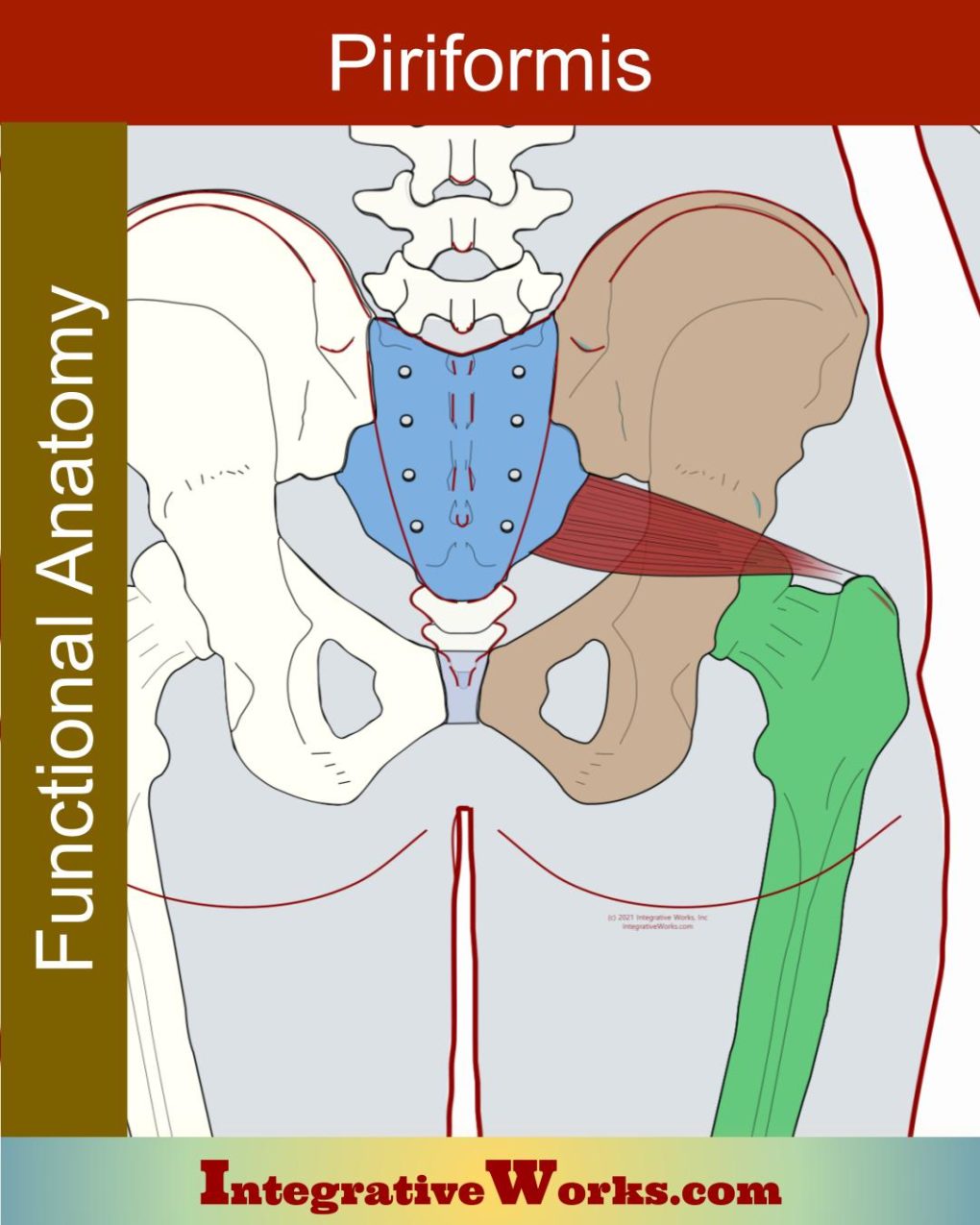
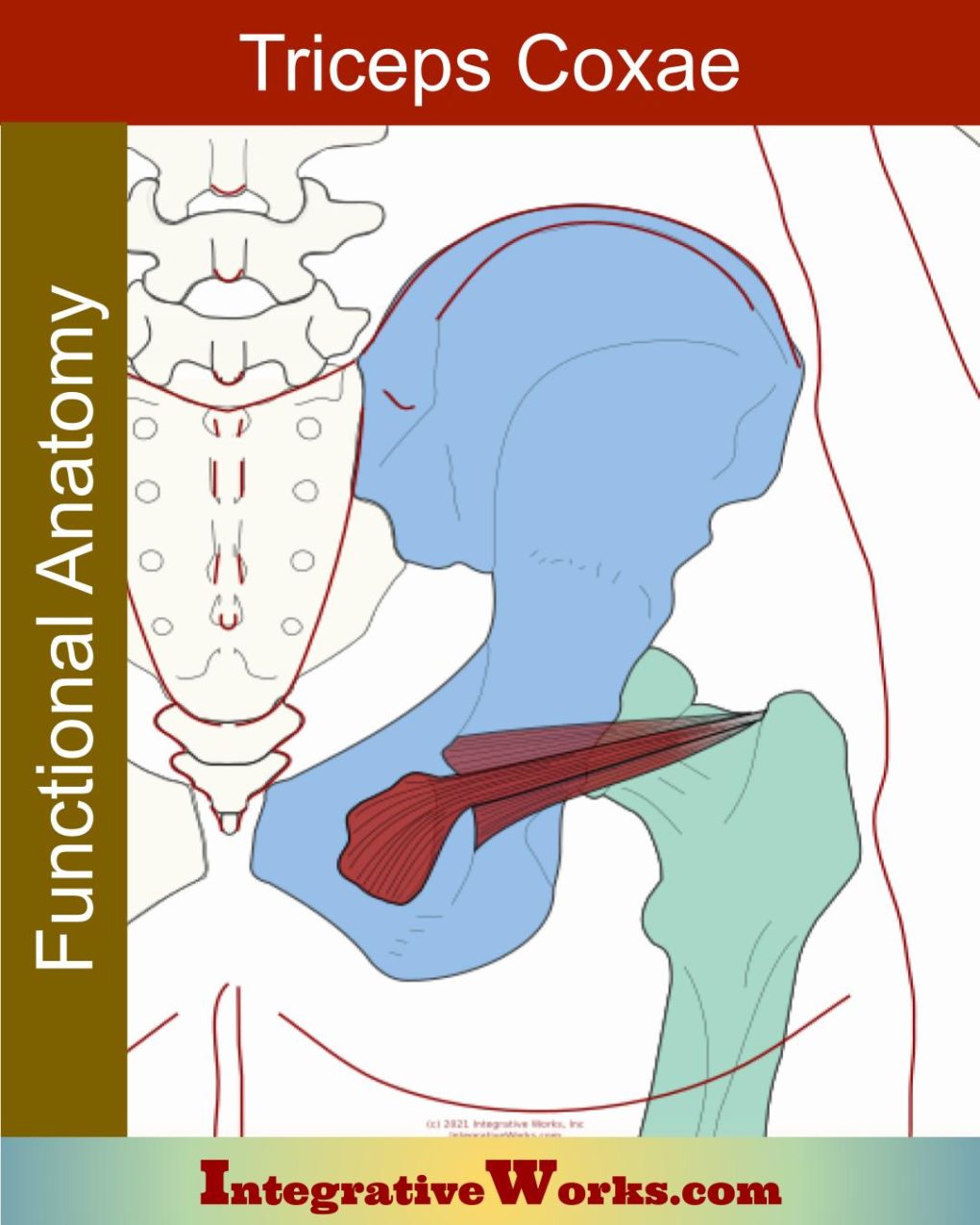
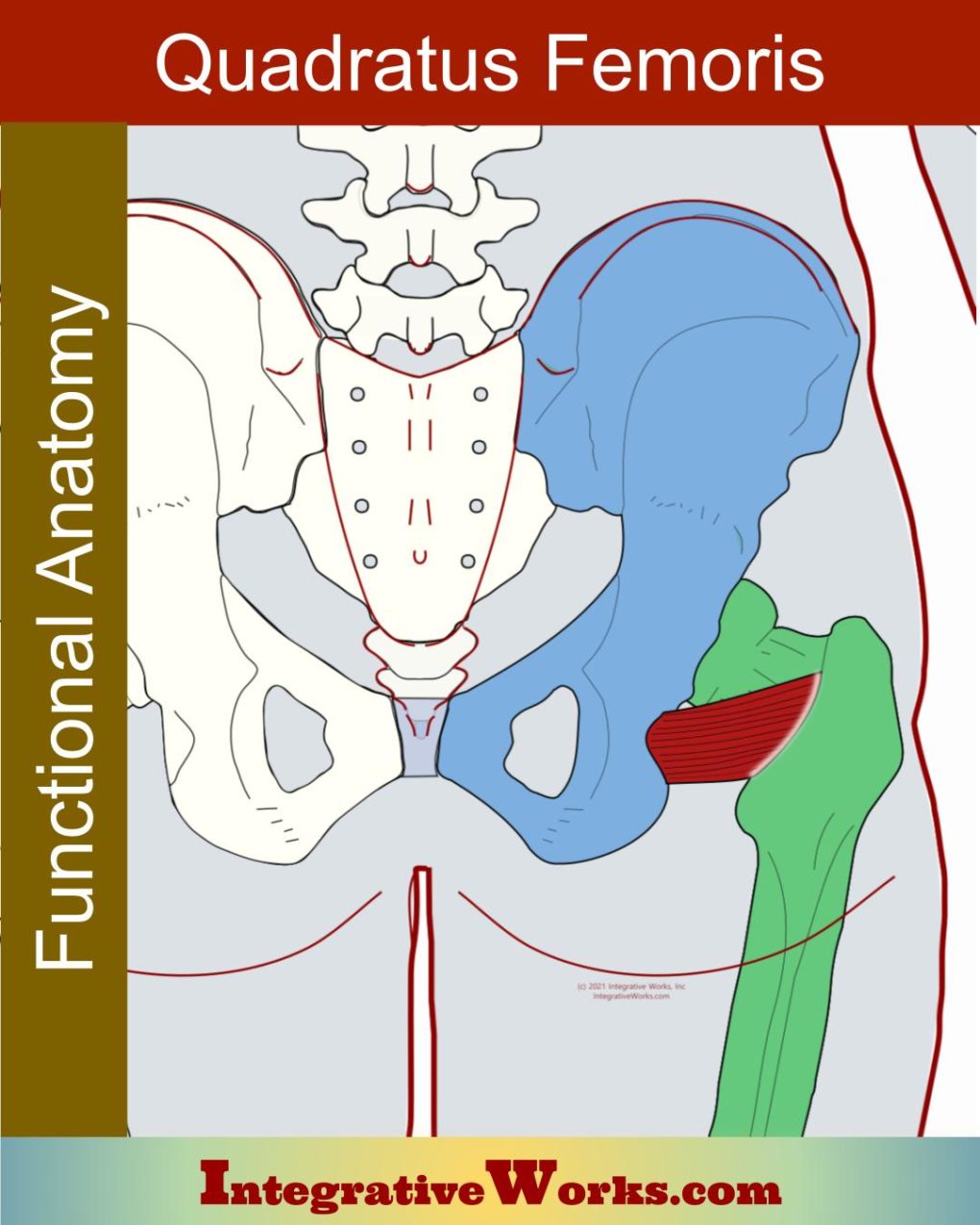
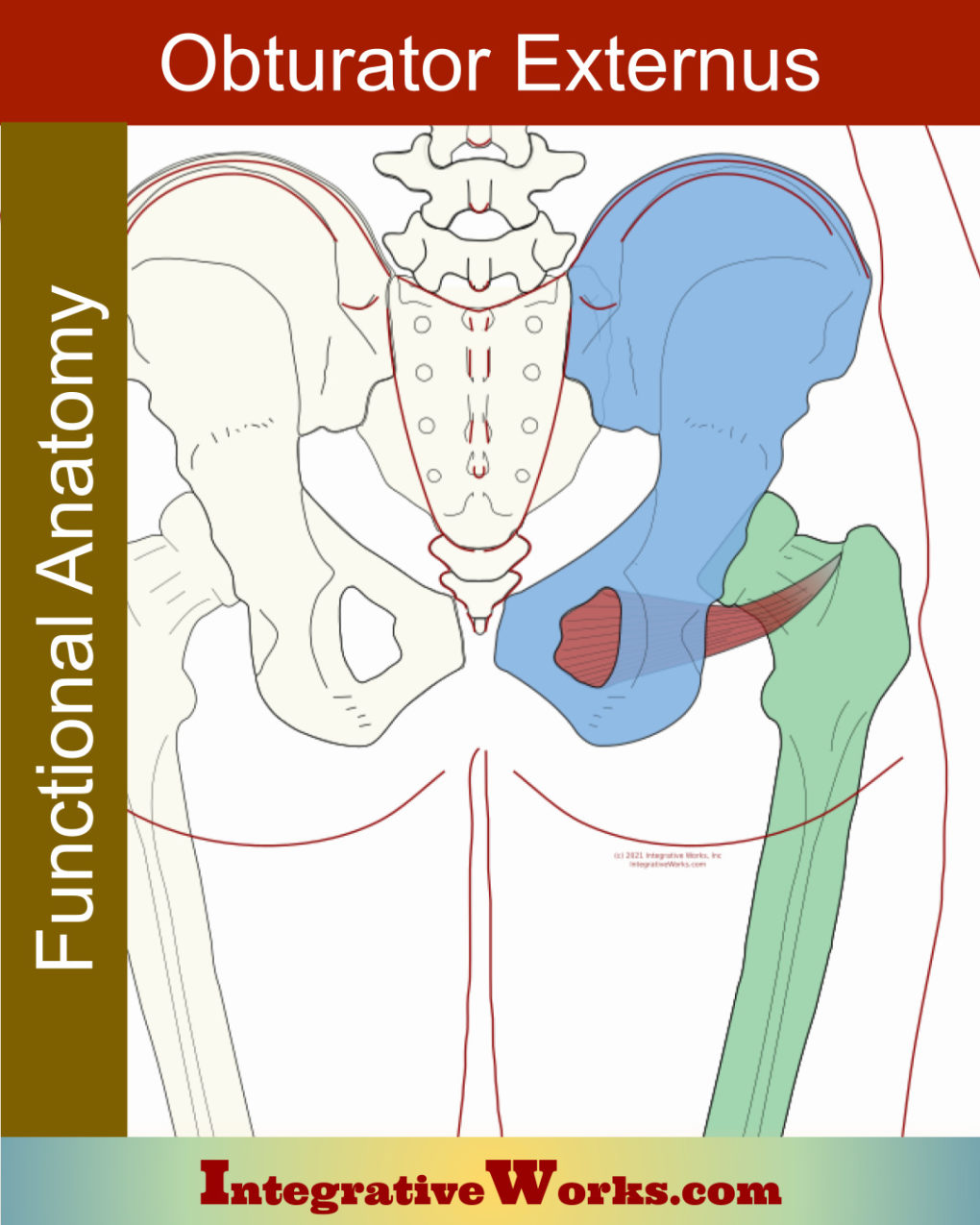
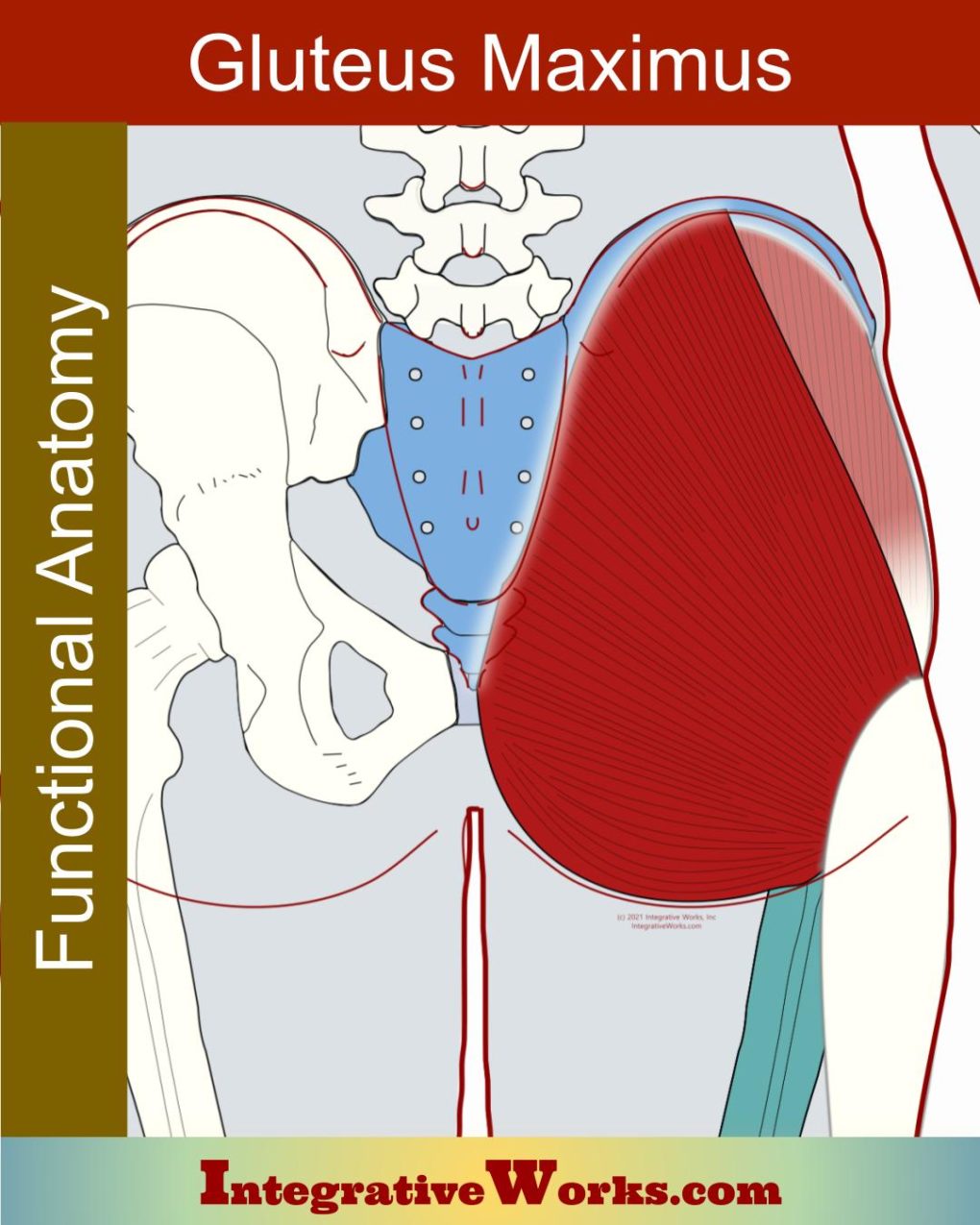
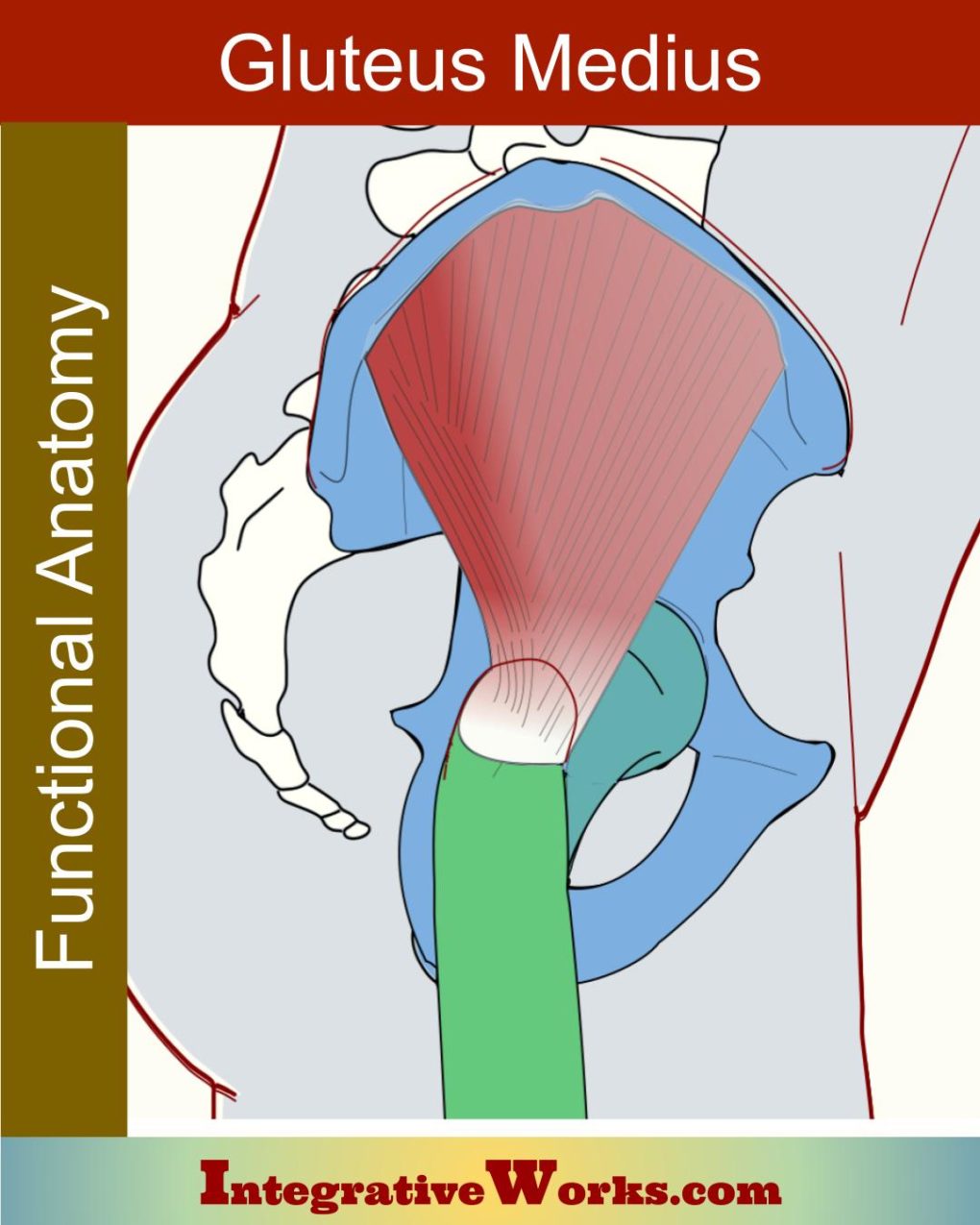
Vastus Lateralis – Functional Anatomy
Overview of Anatomy The functional anatomy of the vastus lateralis is largely uncomplicated. However, it has frequent and subtle variations. The fascia lata thickens and forms the iliotibial tract, along the lateral aspect of the vastus lateralis. Origin Insertion Function Nerve The vastus lateralis is the largest and strongest quadriceps muscle. Primarily, it extends the […]